In an electric motor, the concept of energy conversion was explained by British scientist namely “Michael Faraday” in the year 1821. The main function of the motor is to convert the energy from one form to another. The alteration of energy can be done through a conductor that carries current in a magnetic field. Once the electrical current, as well as a magnetic field, generates the torque then the conductors begin revolving. After that in 1832, the DC machine was invented by a British scientist namely “William Sturgeon”. But, this machine was not used in any applications due to its cost. At last, Frank Julian Sprague has invented the first electric motor in the year 1886. This article discusses brief information regarding an electric motor.
What is an Electric Motor?
An electric motor definition is, a motor is an electromechanical device, used to alter energy from electrical to mechanical. The output energy from the motor can be used to rotate fan, the impeller of the pump, blower, lift materials, and to drive compressors. These motors use different power sources like a direct current from rectifiers, batteries, motor vehicles otherwise alternating current sources like electric generators, power grids, and inverters. The electric motor diagram is shown below.

electric-motor
Construction of Electric Motor
The construction of an electric motor is shown below. This motor can be built with different components like rotor, stator, air gap, windings, and commutator.
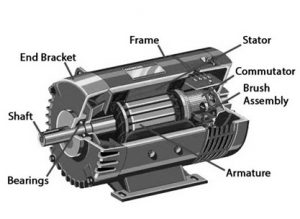
electric-motor-construction
1). Rotor
It is a moving part in an electromagnetic system of motor, generator otherwise alternator. The rotor in a motor plays the main role in rotating the shaft to produce mechanical energy. Usually, the rotor contains conductors which are placed to hold currents as well as to interact with the magnetic field within the stator. Because of its rotation, the communication between the magnetic fields & windings will generate torque in the region of the rotor axis.
2). Bearings
The bearings play an essential role within the motor by providing the support for the rotor to turn on its axis. The electric motor’s shaft can be increased using the bearings to the motor’s load. When the load forces are applied at the external side of the bearing, this load is called as overhung.
3). Stator
This is an inactive part of a rotary system in the motor. It is available in generators, biological rotors, mud motors, and sirens. The stator includes windings, permanent magnets or slight metal sheets known as laminations. These are used for decreasing energy losses.
The stator in a motor provides a rotary magnetic field to drive the rotary armature. Similarly in a generator, it changes the rotary magnetic field into electric current.
4). Air Gap
The gap between the rotor and the stator in the motor is known as the air gap. The air gap effect mainly depends on the space. It is the main source of the low power factor in the motor. When the space between the rotor & stator increases, then magnetizing current will also be increased.
5).Windings
Windings are nothing but wires that are placed within the coils. Usually, these are enclosed approximately a stretchy iron magnetic core to make magnetic poles energized through the current. In the motor, the copper winding is commonly used material as they carry electrical load properly.
6). Commutator
A commutator is one kind of rotating electrical switch and it reverses the direction of current flow among the rotor & the exterior circuit. This is used in a special type of motors and generators. The commutator is built with a cylinder, collected of numerous metal contact sections on the rotating armature of the machine. The commutator is used to connect the brushes with the coil and the shape of the commutator is look like a half ring, designed with copper.
Working of Electric Motor
The working principle of an electric motor is electromagnetic induction. Place the two magnets in some distance with each other, and make a loop using a small conducting wire. Arrange this loop in between two magnets and connect the two loop ends to the terminals of the battery.
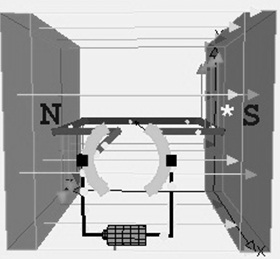
electric-motor-working
Once the flow of current through the circuit is applied, then the loop starts moving due to the current-carrying conductor interfaces with the magnetic field. To make the wire loop as a magnet, the loop one side is attracted to the North Pole and another side is attracted to the South Pole of the magnet. So the loop rotates continuously.
Types of Electric Motor
The classification of the electric motor can be done based on different considerations like the type of power source, construction, and application. In addition to AC types and DC types of motors, there are some more types of motors available like brushed, brushless, 1-phase, 2-phase, or 3-phase, air-cooled/liquid-cooled. General electric motors that have typical dimensions, as well as characteristics, give suitable mechanical power to use in industries.
- AC Motors
- DC Motors
AC Motors
The main function of the AC motor is to change the current from alternating to mechanical with the help of electromagnetic induction. This motor works with alternating current and the main parts of this motor are the rotor & stator. The stationary part in the motor is stator whereas the rotating part is rotor. This motor may be a single-phase motor/three-phase motor. Single-phase motors are mainly used in small power conversion whereas the three-phase motor is used in huge power conversion. To know more regarding this concept please refer to this link: AC Motor
DC Motors
A DC motor is a kind of rotary electrical machine, used to convert the energy from DC to mechanical. Most of the motors depending on the generated forces from the magnetic field. The internal mechanism of these motors is either electronic or electromechanical to change the flow of current direction in the motor. This motor speed can be controlled using either by altering the potency of current or a variable supply voltage within the field windings. To know more regarding this concept please refer to this link: DC Motor
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of the electric motor are
- These motors cost is reasonable compared with other engines like fossil fuels. However, the horsepower (hp) rating is similar to both.
- The lifespan of electric motors is longer.
- The capacity is up to 30,000 hrs but it needs little maintenance
- These are very efficient & its controlling capability allows automatic start and stops functions.
- They don’t use fuel or battery service.
The disadvantages of the electric motor are
- Large motors are not simply movable & consideration must be made for the precise current and voltage supply.
- It has a more efficient performance.
Applications of Electrical Motor
Electrical motors are used in various applications which include the following.
- These motors are used in fans, blowers, pumps, turbines, ships, tools used in machines, movers, rolling mills, compressors, alternators, and paper mills.
- These are the most important devices in Heating Ventilating & Cooling (HVAC) equipment, motor vehicles, and home appliances.
- These are used in industrial equipment like mills, fork mill trucks, letches, robots, winches, and hoists.
Thus, an electric motor an electro-mechanical device and it is one of the main developments in the engineering field. This device changes the energy from electrical to mechanical. There are different kinds of motors available in the markets which are used in various applications. Here is a question for you, who invented electric motor?