The name of Hipot testing is taken from the “high potential” that they produce to achieve dielectric withstand & insulation resistance tests. So this testing has long been a standard process for different kinds of equipment. A lot of hipot testers also offer precise, low-resistance, high-current outputs and low-resistance measurements for testing ground bond integrity & ground resistance. At present, most advanced hipot testers use electronic … [Read more...]
Diversity Factor : Calculation, Table, Advantages, Disadvantages & Its Applications
In substations, a huge amount of electricity cannot be stored for use later, thus it is required to produce electricity according to consumer demands. The different electrical sources at the substation should be capable of accomplishing the requirements of load at all times. If all the electrical loads that are connected to the substation or generator demand load concurrently, then it is not feasible to accomplish the requirements of the load. But the … [Read more...]
SF6 Circuit Breaker : Construction, Working, Types, Maintenance & Its Applications
A circuit breaker is one type of protection device used to give protection to the electrical system against fault currents. The main function of the circuit breaker is to stop the flow of current to guard equipment by preventing fire risk. There are different types of circuit breakers. A circuit breaker is significant in electrical systems for security & reliability. If any fault happens, the circuit breaker protects people against electrical shocks … [Read more...]
Reverse Polarity : Circuit, Working, Causes, Symptoms, Advantages & Its Disadvantages
The term ‘Polarity’ can be defined as when an entity has two different & reverse poles that can either repel or attract each other. The term ‘polarity’ is used in different fields like electricity, electronic signaling, chemistry, and magnetism to explain the flow of electrons. Similarly, reverse polarity is quite opposite to it which means it is a condition where an outlet’s electrical wires are connected simply in reverse. Whenever the two poles are … [Read more...]
Protection Relay : Working, Circuit, Types, Codes, Functions & Its Applications
A relay is a four-terminal electrical switch, used to control any electrical circuit with an independent low-power signal and also to control various electrical circuits with a single signal. The terminals of the relay mainly include; common, coil, NO (normally open) & NC (normally closed). Generally, in long-distance telegraph circuits, relays were employed as signal repeaters. After that, these were used widely in telephone exchanges and early … [Read more...]
Single Phase Inverter : Working, Types, Connection with Arduino & Its Applications
A power electronic device that is used to change power from DC to AC form at the necessary frequency & voltage output is known as an inverter. The inverter input is a fixed DC voltage that is attained from the batteries & the inverter output is normally a variable or fixed frequency alternating voltage. The inverter is designed as separate equipment to use in different applications. Inverters are available in different types based on the switching … [Read more...]
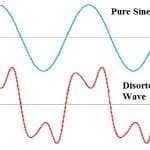
Total Harmonic Distortion : Measurement, Implications,Example, Advantages & Its Disadvantages
In an increasingly interconnected and technology-driven world, the quality of electrical power and the reliability of electronic devices are paramount concerns. As we rely on a vast array of electronic equipment for various applications, from home appliances to industrial machinery, the integrity of electrical signals becomes crucial. One critical aspect in assessing the purity of these electrical signals is Total Harmonic Distortion (THD). THD is a … [Read more...]
Latching Relay : Working, Circuit, Wiring, Types & Its Applications
Generally, normal switches are used at present to open or close an electrical circuit manually. Similarly, a Relay is one type of electromechanical switch used for connecting or disconnecting two electrical circuits. But a relay utilizes an electrical signal for controlling an electromagnet to fix or separate another circuit. Relays are used where a particular circuit or various circuits needs to control with a low-power signal. Relays are available in … [Read more...]
Electrical Wiring : Materials, Colors, Types and Their Differences
A wire is an electrical conductor that carries electricity where the conductor of wire is made with aluminum or copper. Similarly, a cable is a set of one or more different wires used to transmit electric current. It is necessary to know different kinds of wires & their characteristics controlled by the NEC or National Electrical Code for different installations & applications. There are many factors that need to be considered for selecting a … [Read more...]
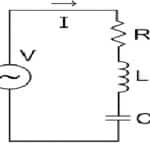
Quality Factor : definition, Formula, Damping, Unit and Its Effects
The Quality Factor ‘Q’ concept was first conceived by an engineer “K. S. Johnson” from the Department of Engineering of Western Electric Company in the United States. He evaluated the quality & performance of different coils. He developed the quality factor concept during his investigation over the course. Surprisingly, his choice of selecting the ‘Q’ letter for the quality factor was made with observation. This concept was applicable in many areas of … [Read more...]