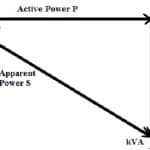
The power factor (PF) in any electrical system can be defined as; the ratio of the real power to the apparent power. Here, real power is measured in kW (kilowatts) and apparent power is measured in kVA (kilovolt amperes). So, the power factor is the measure of how efficiently the power is utilized within an electrical system. A low power factor (LPF) means that the electrical system is not completely using the power so that system efficiency can be reduced … [Read more...]
Turbo Generator : Construction, Working, Types, Specifications & Its Applications
The history of the turbo generators dates back to late 1800s when Charles Algernon Parson developed the first steam turbine which uses high pressure stream to rotate a shaft that was connected to the generator. In simple terms, the first turbo-generator is an electrical generatorthat was powered by water turbines. The breakthrough allowed for much more efficient generate of electricity compared to the traditional steam engines which were bulky and had … [Read more...]
Demand Factor : Factors, Load Calculation & Its Applications
At present, electrical energy is a significant resource, so it is increasing day by day. When electrical demand increases, then the distribution system should have sufficient capacity to meet that demand. So this capacity is measured by engineers with the demand factor (Df) formula. It is a very significant factor for engineers, homes, businesses, etc. Generally, it is measured every month but most companies choose to measure it periodically at shorter … [Read more...]
Residual Current Device : Circuit, Working & Its Applications
Electricity is incredibly useful everywhere but a lot of people die or injured at home or in industries due to electrical accidents. These accidents can be prevented by installing residual current protection devices in the consumer unit of the house. So these devices can save lives by guarding you & your family against electric shock & provides some protection from fire. This device turns off the electric power supply in a fraction of a second if … [Read more...]
Electron Flow : Working, Formula & Its Differences
An Electron (e–) is a subatomic particle with a negative electric charge where the atom is made with three particles like protons, electrons & neutrons. All these three particles can form the nucleus of an atom. Every electron carries 1 unit of negative charge like 1.602 x 10-19 coulomb & it has an extremely small mass like 9.10938 x 10-31 kg as compared with a proton and a neutron. An Electron belongs to the first invention of the lepton particle … [Read more...]
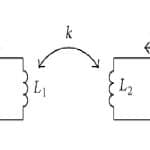
Coefficient of Coupling : Derivation, Working & Its Example
For inductor-coupled circuits, the coefficient of coupling is a significant factor to decide the amount of coupling between the inductively coupled coils. These coils are coupled with the magnetic flux. If one inductor’s total magnetic flux is coupled with the other inductor then it is known as perfect coupling. In this situation, this coupling (K) is expressed as 1 which means 100% coupling. The mutual inductance mainly depends on the coefficient of … [Read more...]
Different Types of Resistors and Its Color Code Calculation
The resistor was invented in 1827 by a mathematician namely “Georg Simon Ohm” at the University of Erlangen. After that, he published several research papers on the transmission of heat within molded circuits & also invented the “ohm law”. After this law invention, there are many types of resistors were developed. At present, we are using different types of resistors in so many electrical and electronic applications. This article provides brief … [Read more...]
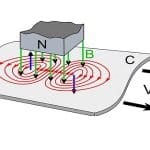
Eddy Current : Working, Advantages, Loss, Braking System & Its Applications
We know that electromotive force & current will generate when the magnetic flux is flowing throughout a coil changes. Similarly, once the magnetic flux is passed throughout a solid coil, then it will induce current & emf. So the induced current through the conducting body is called the eddy current. This current is named an eddy current because of the flow of the current look like eddies/whirlpools. This article discusses an overview of an eddy … [Read more...]
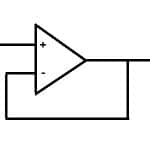
Voltage Follower : Circuit, Working, Purpose & Its Applications
The operational amplifier or op-amp is a versatile & very efficient device. The op-amp is used to amplify the weak signal and it can be made simply into various forms based on the requirements of the circuit. One of the forms is the voltage follower. Here voltage follower is mainly used for isolating the signal as well as improving load capacity and this is also known as a unity-gain amplifier, isolation amplifier, or buffer amplifier. In a voltage … [Read more...]
Phase Shifting Transformer : Construction, Working & Its Applications
At present, the power generation landscape as well as the energy market is growing, so controlling the power flow capacity is very important. So phase shifting transformer is an essential component used to enhance AC network efficiency, protect HV equipment & transmission lines from thermal overload, enhance transmission system stability & control the flow of power between various networks. Compared to fixed power transformers, these are extremely … [Read more...]